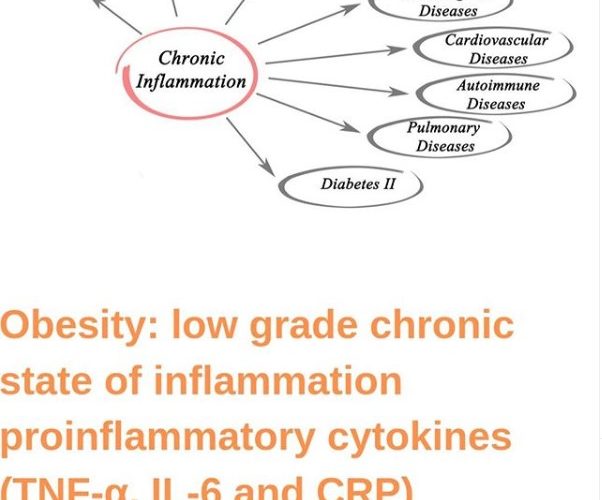
Obesity is characterized by a low-grade chronic state of inflammation in which the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and CRP are increased. It is a state in which there is an over-accumulation of subcutaneous and/or abdominal adipose tissue.
This adipose tissue is no longer considered inert and mainly devoted to storing energy; it is emerging as an active tissue in the regulation of physiological and pathological processes, including immunity and inflammation. Adipose tissue is also implicated in the development of chronic metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus or cardiovascular disease.
Obesity can therefore be caused by inflammatory and metabolic diseases. Diet or dietary patterns as well play critical roles in obesity and other pathophysiological conditions. It is therefore recommended for one to have a healthy diet and other nutrients that are generally considered to be beneficial.